For a long time, data recovery from SSD drives was very complicated and take too much time. For one SSD case engineer should waste around 1 week of his time, trying to detect the correct order of memory chips, eliminate all controller preparations and finally, build image with user data.
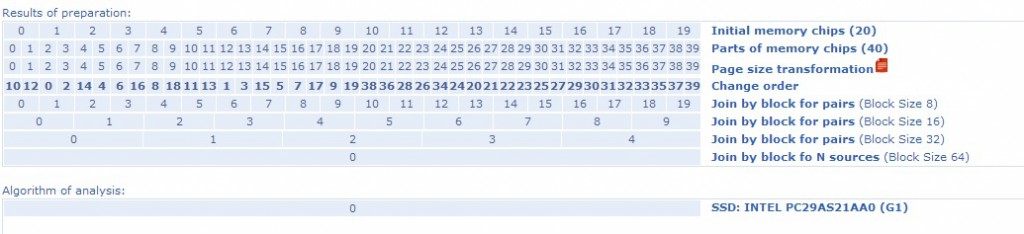
For example, in this solution from GSC, you can see – how may joining preparation contain a common Intel SSD drive:
And of course,before you will start to make any preparation, you must be sure in correct order of memory chips reading from this drive, because if order will be incorrect, you will not build the whole image of drive. Finally, the whole procedure of data recovery from such SSD should be like this one:
1. Try to find markers on PCB with chip order;
2. Unsolder all memory chips;
3. Try to correct ECC errors;
4. Try to find correct joining of memory chips and parts;
5. Apply algorithm for image building;
6. In case of a huge number of ECC or in case of shifts presented between blocks, you will not get folder structure, and you will need to spend additional time for data analysis and partition recovery.
As you can see, this way is not too easy.
But the main problem of the most modern SSD is that they have full hardware encryption. It means, that if you will unsolder memory chips, and will try to read data from them you will found that data is hidden by encryption, and instead file headers you will get encrypted pattern or random byte trash. Or other situation – drive is encrypted by user password, and block access to file system. In this situation, when SSD crypt all files with AES-128 key, the recovery become impossible.
That’s why, starting from PC-3000 Flash SSD Edition 6.0, ACE lab developers add new functionality of Active Utilities. This new way of SSD recovery is very simple, and required only a few minutes! All SSD drives have similar to a common HDD architecture. They also have ROM and RAM chips, they have service area, where all service modules and structures are situated. And of course, they have main microprogram and translator, that allow user to get access to his data.
The most typical problem of all SSD drives is problem with main microprogram or with translators, and functionality of Active Utilities Set allow us to restore this service structures, and provide access to User Area.
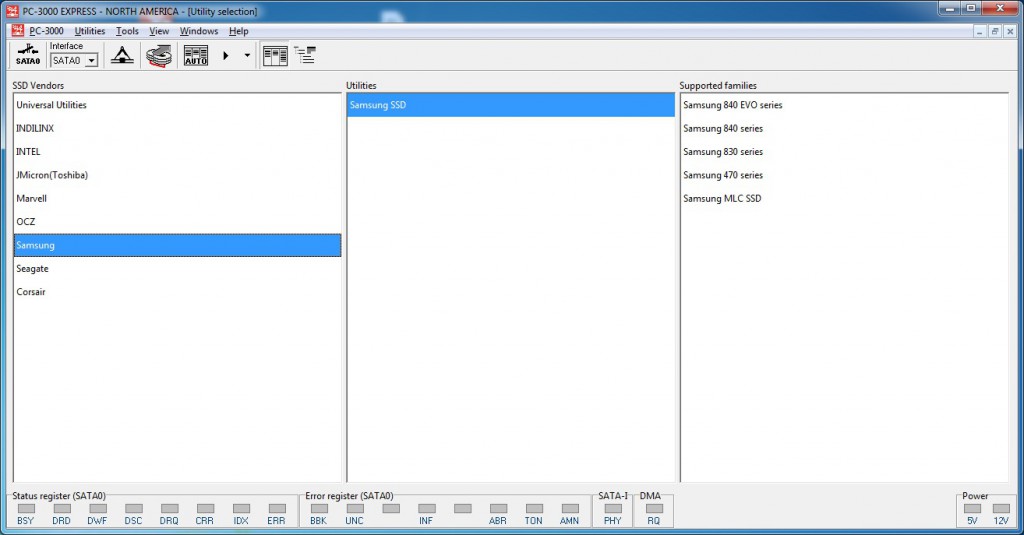
For getting access for PC-3000 Active Utilitys functionality, user should have PC-3000 Portable 2.0, PC-3000 UDMA-E or PC-3000 Express. This board is required, because unfortunately, Windows can block this commands, and do not allow users work with ATA commands on state-connected drive. That’s why unfortunately, common SSD connection through SATA port of PC motherboard is not working, and that’s why current way of recovery required any of PC-3000 controllers for HDD recovery.
Everything that you should do for such case recover:
- Plug your SSD drive and launch Special Utility;
- Activate Tech Mode or build translator;
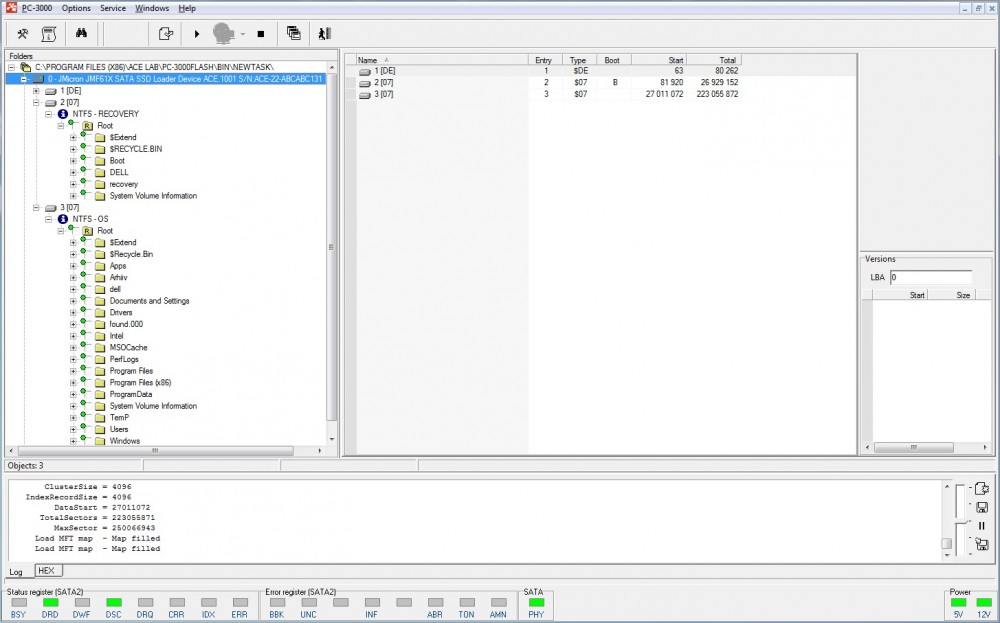
- Get full access to data.
Active Utility allow to make:
- Switching drive into technological mode and providing access to user data even if main SA structures are damaged
- Restore translator in case if it is damaged;
- Rewrite firmware or microcode;
- Read dumps from memory chips without chip desoldering;
- Reset/set user and factory passwords;
- Make factory reset with full service information rewriting, and restoring default SSD functionality;
- Edit SDD passport ID;
- Make testing of NAND memory chips installed on SSD;
- Remove passwords.
The number of supported SSD drives is grown up with each new release of PC-3000 SSD software, so keep to regularly check our F.A.Q, and find there latest educational video with descriptions of Utility functions! ![]()